Tritium Fuel Cycle 0-D System Model¶
1. Introduction to the Tritium Cycle System¶
The fusion reactor's tritium fuel cycle is architecturally divided into two highly coupled systems: the inner fuel cycle and the outer fuel cycle.
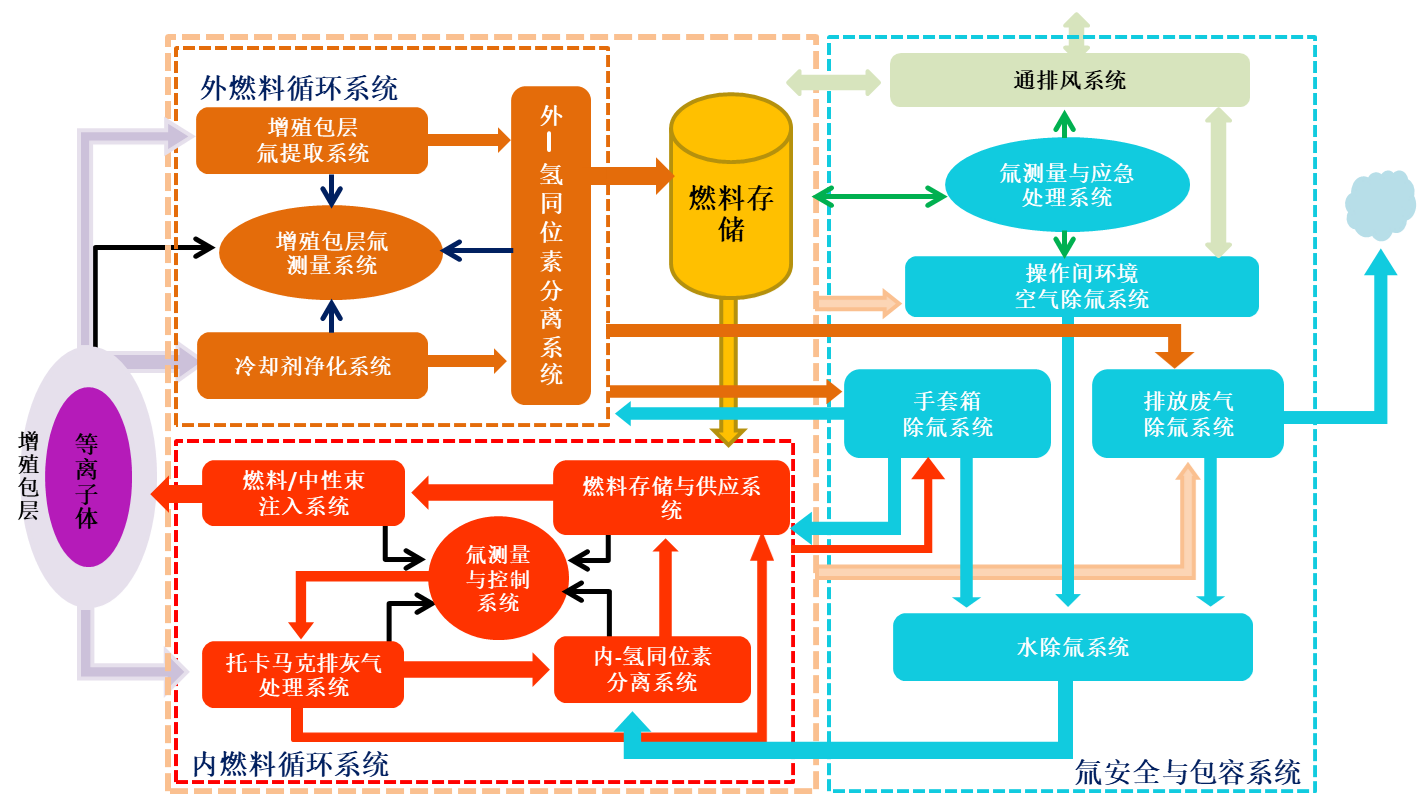
1.1. Inner Fuel Cycle¶
This is a high-throughput, fast closed-loop circuit that processes unburnt fuel. Its material flow path is as follows:
1) Fuelling: The cycle begins at the Storage and Delivery System (SDS). High-purity D-T fuel is injected into the Tokamak vacuum chamber (Plasma) via the Fueling System (FS).
2) Exhaust: In the plasma, only a small amount of fuel undergoes fusion. The majority of unburnt fuel, fusion products (helium ash), and impurities are directed to the Divertor area.
3) Pumping: The Vacuum Pumping System (Pump_System) extracts these hot exhaust gases.
4) Purification (TEP): The exhaust gas is sent to the Tokamak Exhaust Processing (TEP) system. Here, TEP performs crucial chemical purification to recover hydrogen isotopes from impurities such as tritiated water (Q2O) and tritiated methane (CQ4).
5) Separation (ISS): The purified hydrogen isotope (Q2) gas mixture is sent to the Inner Isotope Separation System (I-ISS), where isotope separation is typically performed using cryogenic distillation.
6) Return: Finally, the separated high-purity D2 and T2 fuels are returned to the SDS, enabling fuel recycling and completing the inner closed loop.
1.2. Outer Fuel Cycle¶
This is a low-throughput, slow loop responsible for producing new fuel to achieve tritium self-sufficiency. Its material flow path is as follows:
1) Breeding: High-energy neutrons from fusion enter the Breeding Blanket, where they react with lithium (Li) in the blanket to breed new tritium.
2) Extraction: The newly bred tritium is removed from the blanket material by the Tritium Extraction System (TES).
3) Permeation & Purification: Simultaneously, a small amount of tritium inevitably permeates into the coolant loop (CL). The Coolant Purification System (CPS) is responsible for capturing and recovering this permeated tritium from the coolant.
4) Collection & Separation: The tritium-rich stream from the TES (e.g., helium purge gas from a solid blanket or permeator product gas from a liquid blanket) merges with the recovered tritium stream from the CPS. Both are transported to the Outer Isotope Separation System (O-ISS) for purification.
5) Replenish: After removing helium and other impurities, the O-ISS sends high-purity tritium to the SDS to replenish the main fuel cycle, completing the plant-wide fuel closed loop.
2. Modelica Example Model¶
The core of TRICYS is a 0-D system model of the tritium fuel cycle. This model abstracts the fusion reactor's tritium fuel cycle system into a series of interconnected subsystems, each representing a key functional module in the actual plant.
A 0-D model means we focus on system-level material flow and inventory changes, rather than detailed spatial distribution. This modeling approach is particularly suitable for:
- System-level tritium inventory analysis
- Fuel self-sufficiency time assessment
- Design parameter optimization
- Operational strategy studies
- Safety assessment
| Abbreviation | Chinese Full Name | English Full Name |
|---|---|---|
Plasma |
等离子体 | Plasma |
Fueling_System |
燃料注入系统 | Fueling System |
Pump_System |
真空泵系统 | Vacuum Pumping System |
TEP_FEP |
托卡马克排气处理 - 前端 | Tokamak Exhaust Processing - Front-End Processing |
TEP_IP |
托卡马克排气处理 - 中间处理 | Tokamak Exhaust Processing - Intermediate Processing |
TEP_FCU |
托卡马克排气处理 - 最终净化单元 | Tokamak Exhaust Processing - Final Cleanup Unit |
I_ISS |
内部同位素分离系统 | Inner Isotope Separation System |
SDS |
储存与输送系统 | Storage and Delivery System |
Blanket |
增殖包层 | Breeding Blanket |
TES |
氚提取系统 | Tritium Extraction System |
O_ISS |
外部同位素分离系统 | Outer Isotope Separation System |
FW |
第一壁 | First Wall |
DIV |
偏滤器 | Divertor |
Coolant_Pipe |
冷却剂回路 | Coolant Pipe |
CPS |
冷却剂净化系统 | Coolant Purification System |
WDS |
水去氚系统 | Water Detritiation System |
3. Further Learning¶
- Quickstart: Run your first simulation
- Basic Configuration: Learn how to configure model parameters
- Parameter Sweep: Systematically study the parameter space
- Sensitivity Analysis: Identify key parameters